INDICATION AND USAGE
HEPZATO (melphalan) for injection, as a component of the HEPZATO KIT, is indicated as a liver-directed treatment for adult patients with uveal melanoma with unresectable hepatic metastases affecting less than 50% of the liver and no extrahepatic disease or extrahepatic disease limited to the bone, lymph nodes, subcutaneous tissues, or lung that is amenable to resection or radiation.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: PERI-PROCEDURAL COMPLICATIONS, MYELOSUPPRESSION
- Severe peri-procedural complications including hemorrhage, hepatocellular injury, and thromboembolic events may occur via hepatic intra-arterial administration of HEPZATO. Assess patients for these adverse reactions during and for at least 72 hours following administration of HEPZATO.
- HEPZATO is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy called the HEPZATO KIT REMS.
- Myelosuppression with resulting severe infection, bleeding, or symptomatic anemia may occur with HEPZATO. Monitor hematologic laboratory parameters and delay additional cycles of HEPZATO therapy until blood counts have improved.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Active intracranial metastases or brain lesions with a propensity to bleed
- Liver failure, portal hypertension, or known varices at risk for bleeding
- Surgery or medical treatment of the liver in the previous 4 weeks
- Uncorrectable coagulopathy
- Inability to safely undergo general anesthesia
- Active cardiac conditions including, but not limited to, unstable coronary syndromes (unstable or severe angina or myocardial infarction), worsening or new-onset congestive heart failure, significant arrhythmias, or severe valvular disease
- History of allergies or known hypersensitivity to melphalan or a component or material utilized within the HEPZATO KIT including:
-
- natural rubber latex
- heparin or presence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
- iodinated contrast not controlled by premedication with antihistamines and steroids
-
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Peri-procedural complications, including hemorrhage, hepatocellular injury, and thromboembolic events have been observed with HEPZATO. Administration of HEPZATO requires general anesthesia and extracorporeal bypass of circulation which may cause life threatening or fatal adverse effects. Ensure the patient is euvolemic but do not overhydrate the patient. Monitor for these peri-procedural complications during and for at least 72 hours following the procedure. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolic events, administer anticoagulation as described in the Instructions For Use (IFU). Due to the risk of bleeding, do not use in patients with uncorrectable coagulopathies and delay treatment with the HEPZATO KIT for at least 4 weeks after surgery or other medical procedure involving the liver. Platelets and clotting factors may be removed during the procedure. Monitor platelets and coagulation parameters as described in the IFU. If life-threatening bleeding occurs during the procedure, reverse anticoagulation as described in the IFU and correct coagulopathy as appropriate. Discontinue anticoagulation with warfarin or other oral anticoagulants prior to the procedure; resume when hemostasis has been restored after the procedure, provided no bleeding complications have been observed. Refer to the Prescribing Information (PI) of the anticoagulant agent for bridging recommendations for anticoagulation prior to surgical procedures. Discontinue drugs affecting platelet function such as aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or other anti-platelet drugs one week before the procedure. Patients with abnormal hepatic vascular (especially arterial supply) or biliary (especially re-implantation of bile duct) anatomy or gastric acid hypersecretion syndromes may be at increased risk of peri-procedural complications or other severe adverse reactions. Screen patients for a history of prior surgeries involving the bile duct to assess whether the patient is an appropriate candidate for HEPZATO KIT and monitor patients for adverse reactions following HEPZATO KIT administration. Procedure-related reductions in blood pressure including severe hypotension can occur, closely monitor blood pressure during the procedure. Patients may require fluid support and vasopressors. To reduce the risk of severe hypotension, assess hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function, and temporarily discontinue ACE-inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, or alpha-1-adrenergic blockers for at least 5 half-lives prior to treatment with the HEPZATO KIT. If necessary, use other short-acting antihypertensive drugs to manage blood pressure during the peri-procedure period.
HEPZATO KIT REMS PROGRAM, The HEPZATO KIT is only available through a restricted program under a REMS, because of the risk of severe peri-procedural complications including hemorrhage, hepatocellular injury, and thromboembolic events defined in the REMS. The HEPZATO KIT should only be used by trained healthcare providers. Important requirements of the HEPZATO KIT REMS include:
- Healthcare settings that dispense and administer HEPZATO KIT must be enrolled, certified, and comply with the REMS requirements.
- Certified healthcare facilities must ensure that healthcare providers who perform the Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion (PHP) procedure are trained on the use of HEPZATO KIT and must only dispense HEPZATO when authorized to do so by the REMS.
- Certified healthcare facilities must ensure that patients are assessed for severe peri-procedural complications during the procedure and for at least 72 hours following the procedure.
Further information is available at www.HEPZATOKITREMS.com or contact Delcath Systems at 1-833-632-0458
Myelosuppression, including thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia have been reported in patients treated with HEPZATO. The risk of hematologic adverse reactions may be increased in patients who have received prior chemotherapy, bone irradiation, or who have compromised bone marrow function. Monitor patients for severe infections, bleeding, and symptomatic anemia. Only administer HEPZATO in patients with platelets >100,000/microliter, hemoglobin ≥10.0 gm/dL and neutrophils >2,000/microliter. Administer transfusions or growth factors as appropriate.
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have occurred in patients who received an intravenous (IV) formulation of melphalan. Immediately terminate hepatic arterial melphalan infusion for hypersensitivity reactions and administer supportive care.
Gastrointestinal adverse reactions including nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are common.
Secondary malignancies including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, and carcinoma, have been reported in patients with cancer treated with alkylating drugs (including melphalan). Melphalan has been shown to cause chromatid or chromosome damage in humans.
Embryo-fetal toxicity, melphalan can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during treatment with HEPZATO and for 3 months after the last dose.
Infertility, melphalan-based chemotherapy regimens have been reported to cause suppression of ovarian function in premenopausal women and testicular suppression in men.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions or laboratory abnormalities are thrombocytopenia, fatigue, anemia, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, leukopenia, abdominal pain, neutropenia, vomiting, increased alanine aminotransferase, prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased alkaline phosphatase, and dyspnea.
USE IN SPECIAL POPULATIONS
- HEPZATO should not be used in patients <35 kg.
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with melphalan and for one week after the last dose.
Your Title Goes Here
HEPZATO KIT:
First and Only FDA-Approved Whole Liver Directed Therapy1
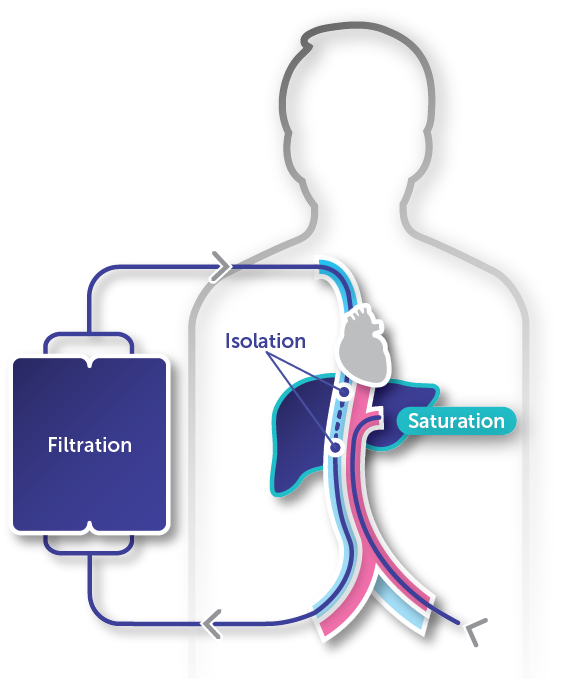
HEPZATO KIT is a unique treatment that delivers high-dose chemotherapy to the entire liver while limiting systemic exposure.1-3
Isolation
Isolating the liver blood supply allows for the benefits of high-dose melphalan while reducing systemic toxicity3,4
Saturation
A 30-minute infusion of high-dose melphalan saturates the liver, effectively delivering treatment to the entire organ1,3
Filtration
A 30-minute washout period limits systemic drug exposure (mean [SD] filter efficiency of 82.7% [14.4%] for the total filtration period)1
Melphalan mechanism of action1,5,6
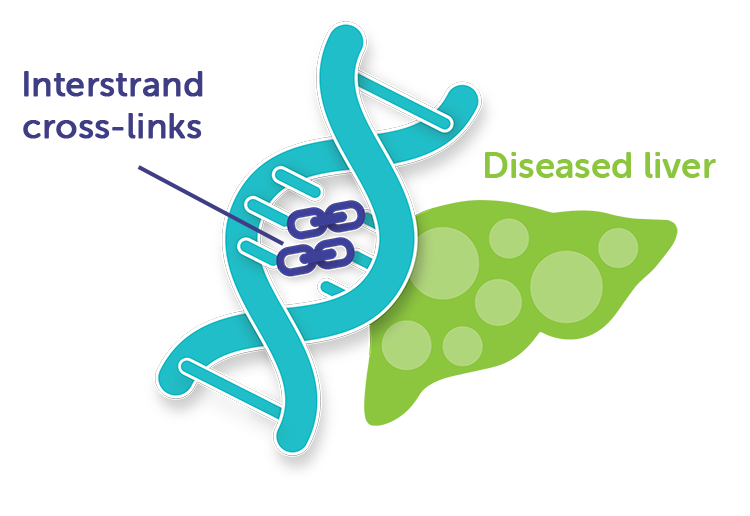
How melphalan works
Melphalan acts by introducing interstrand cross-links into DNA. It is active against both resting and rapidly dividing tumor cells.1
You May Know Melphalan But Not Like This
HEPZATO KIT delivers the potency of high-dose melphalan directly into the liver. Melphalan causes rapid and irreversible DNA damage that results in cancer cell death.1
- Melphalan has been approved and used in the United States since 19641
See How HEPZATO KIT Works
Click play to discover how HEPZATO KIT delivers treatment with high-dose melphalan to the whole liver in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma
Delivering an Innovative Treatment With a Well-Trained Team
HEPZATO KIT is available only through a restricted program under a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) called the HEPZATO KIT REMS.
Treatment with HEPZATO KIT involves training and a team approach. All procedure team members complete a REMS training. HEPZATO KIT procedure team members include2,a:
Interventional radiologist
Leads and performs the vascular interventional procedure2
Perfusionist
Establishes, monitors, and controls the extracorporeal pump and veno-venous bypass circuit2
Anesthesiologist
Manages sedation, analgesia, and respiratory and cardiovascular support2
Other clinical team members involved with HEPZATO KIT treatment include the medical/surgical oncologist, pharmacist, chemotherapist, and intensivist.2

Medical/surgical oncologist

Pharmacist

Chemotherapist

Intensivist
FOCUS Study Highlights
What was the FOCUS Study?
FOCUS was a multicenter, open-label trial that evaluated the efficacy and safety of melphalan delivered with the HEPZATO KIT in patients with unresectable metastatic uveal melanoma (mUM) predominately involving the liver.1
- Primary efficacy end point: Objective response rate (ORR)1
- Key secondary end point: Duration of response (DoR)1
More Than 1/3 of Patients Responded to Treatment With HEPZATO KIT1, 12
ORR reported in FOCUS was 36.3% (n = 33)1
- Complete response (CR): 7.7% (n = 7)1, 12
- Partial response (PR): 28.6% (n = 26)1
Median DoR in responders (n = 33) was 14 months1, 12, c
ORR (CR or PR) in FOCUS1, 12
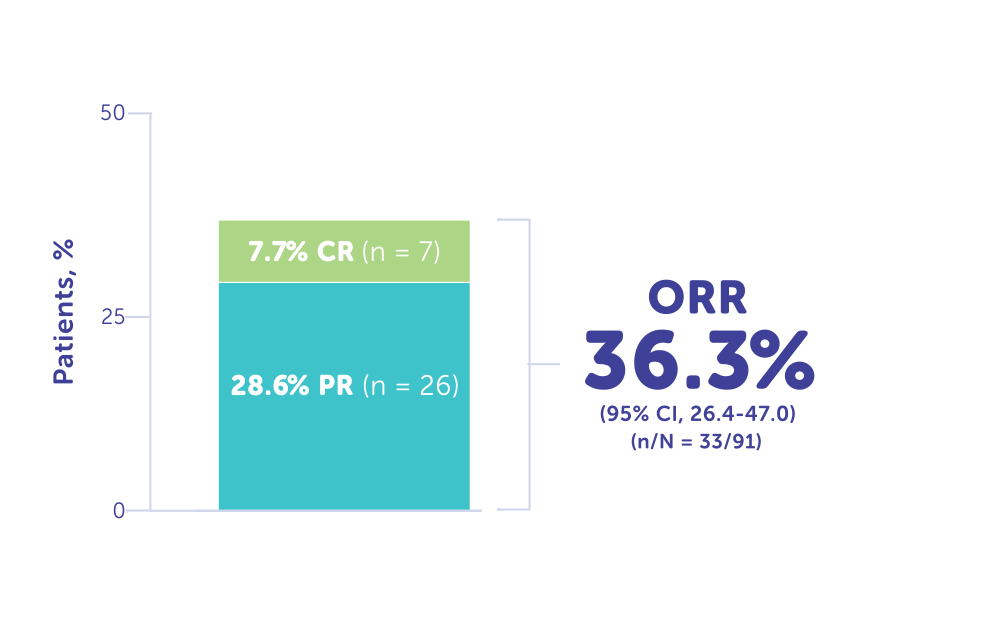
Responders in FOCUS trial (n = 33)1, 12

In an analysis of prespecified subgroups from FOCUS, ORR remained consistent despite presence of extrahepatic lesions, prior therapy, and extent of liver involvement3,13,d
CR: Disappearance of all target lesionsa
PR: ≥30% Decrease in the sum of the long axis diameter of tumor target lesionsb
aAny pathological lymph nodes (target or nontarget) must be <10 mm in short-axis diameter. For nontarget lesions, disappearance of all nontarget lesions and normalization of tumor marker level.7
bUsing the baseline sum as reference.7
cCalculated using Kaplan-Meier method.1
dThe subgroup analysis from the FOCUS trial is exploratory, and results are descriptive.
FOCUS Study Design1
Study patients
95 Patients were enrolled into the HEPZATO KIT arm; 91 patients received treatment.1,a
Key exclusion criteria1
- Metastases occupying ≥50% of the liver parenchyma
- Unable to undergo general anesthesia
- ECOG PS ≥2
- Platelet count <100,000/μL
- Absolute neutrophil count <1500/μL
- Hemoglobin level <10 g/dL
- Child-Pugh class B or C cirrhosis
- Hepatitis B or C infection
ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status.
Treatment schedule
Patients received a dose of 3 mg/kg of melphalan using the HEPZATO KIT every 6 to 8 weeks for up to 6 treatment cycles.1,a
- Patients received a median of 4 treatment cycles (range, 1-6 cycles)
- The maximum of 6 treatment cycles was received by 37% of the 91 treated patients
aBased on ideal body weight (IBW; maximum total dose, 220 mg).
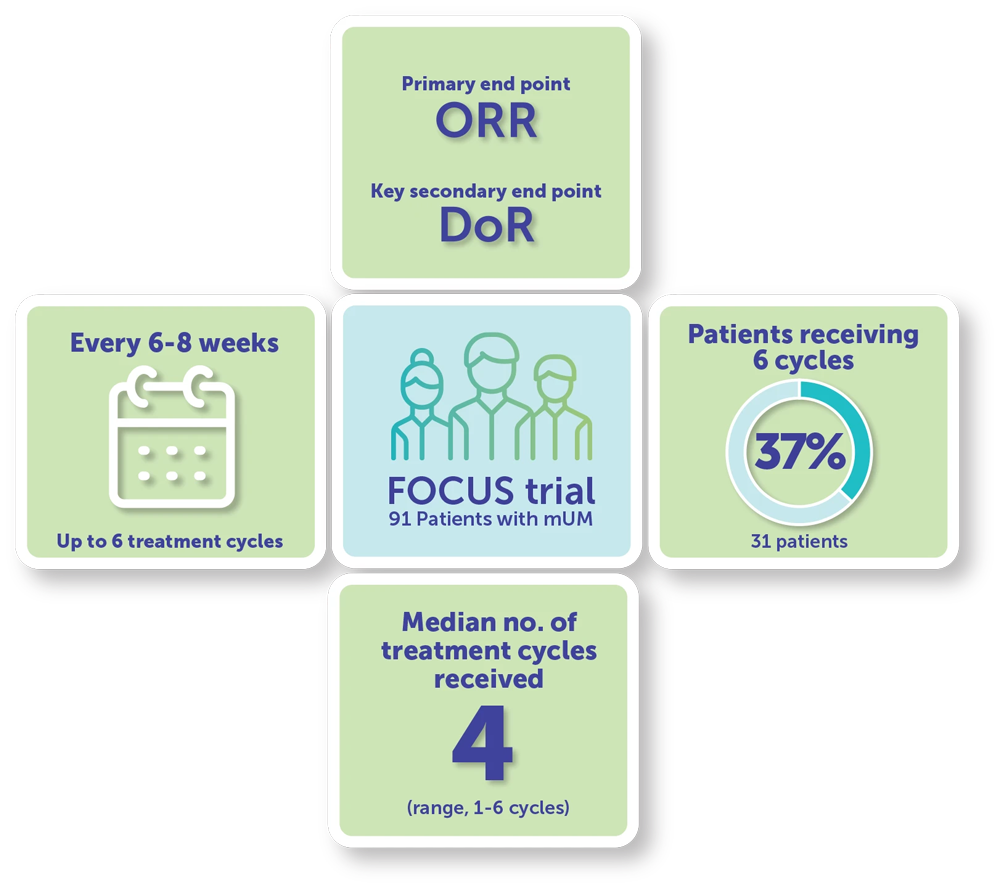
Want to know more about the FOCUS Study?
HEPZATO KIT: Demonstrated Safety and Tolerability1
Most common adverse events (>30% of patients)1
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
All adverse events observed at a frequency of >10% in patients treated with HEPZATO KIT (N = 95)1
aRepresents a composite of multiple, related preferred terms.
Serious adverse events occurred in 45% of patients who received treatment with HEPZATO KIT1
Serious adverse events occurring in ≥2% of patients were thrombocytopenia (10%), neutropenia (8%), febrile neutropenia (7%), platelet count decreased (6%), leukopenia (4.2%), cardiac arrest (3.2%), neutrophil count decreased (2.1%), hypoxia (2.1%), pleural effusion (2.1%), pulmonary edema (2.1%), and deep vein thrombosis (2.1%).1
Fatal adverse events occurred in 3 patients (3.2%) who were treated with HEPZATO KIT; these included cardiac arrest, acute hepatic failure, and bacterial peritonitis and were deemed not to be related to HEPZATO KIT treatment.1,8
HEPZATO KIT treatment was permanently discontinued because of adverse events in 18% of patients, with neutropenia being the most common reason (3.2%).1
Frequently Asked Questions
References:
1. HEPZATO KIT. Package insert. Delcath Systems, Inc. 2023. 2. HEPZATO KIT. Instructions for use. Delcath Systems, Inc. 2023. 3. Quadri HS, Payabyab EC, Chen DJ, Figg W, Hughes MS. Percutaneous hepatic perfusion with melphalan for unresectable liver metastasis. Hepatoma Res. 2016;2:197-202. 4. Ferrucci PF, Cocorocchio E, Bonomo G, Varano GM, Della Vigna P, Orsi F. A new option for the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Percutaneous hepatic perfusion with CHEMOSAT delivery system. Cells. 2021;10(1):70. 5. Rycenga HB, Long DT. The evolving role of DNA inter-strand crosslinks in chemotherapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;41:20-26. 6. Ramnani D. Metastatic malignant melanoma. WebPathology, LLC. Accessed November 9, 2023. https://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=243&n=30. 7. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(2):228-247. 8. Delcath Systems Inc. Data on file. 2.5 Clinical overview: Melphalan/HDS; hepatic-dominant ocular melanoma. 2022. 9. Krantz BA, Dave N, Komatsubara KM, Marr BP, Carvajal RD. Uveal melanoma: Epidemiology, etiology, and treatment of primary disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017;11:279-289. 10. Eschelman DJ, Gonsalves CF, Sato T. Transhepatic therapies for metastatic uveal melanoma. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2013;30(1):39-48. 11. Harbour JW. A prognostic test to predict the risk of metastasis in uveal melanoma based on a 15-gene expression profile. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1102:427-440. 12. Zager JS, Orloff M, Ferrucci PF, et al. Efficacy and safety of the melphalan/hepatic delivery system in patients with unresectable metastatic uveal melanoma: results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 3 study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024;31(8):5340-5351. 13. Wheater M, Orloff MM, Ferrucci PF, et al. Subgroup analysis of FOCUS phase 3 trial efficacy results. Paper presented at: European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress; September 14, 2024; Barcelona, Spain.




